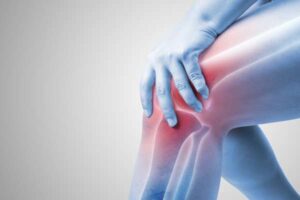
Exploring BPC-157’s Role in Knee Injury Recovery
Exploring the Potential of BPC-157 in Healing Knee Injuries The quest for more effective treatments for knee injuries is increasingly focusing on peptides like BPC-157,

Researchers are likely familiar with the role peptides play in enhancing physical performance; however, their efficacy extends significantly to peptides for injury repair. This document highlights the broad advantages of peptides in tissue regeneration and injury recovery, with a focus on injury repair.
We explore how peptides for injury repair can accelerate healing, reduce inflammation and have a positive impact on gastrointestinal health. This overview aims to enhance understanding of peptides’ therapeutic uses, particularly for injury repair, in medical research.
For Germany researchers focusing on sports medicine, bodybuilding, and general physical fitness, understanding the mechanisms behind muscle and connective tissue injuries is paramount. Individuals engaged in these activities are highly susceptible to strains and sprains, affecting ligaments and tendons and leading to significant discomfort and disruption in training regimes.
Connective tissue injuries, characterized by slower repair processes, initially present inflammation and pain, followed by cell regeneration and, eventually, remodeling. Efficient recovery strategies are crucial to mitigate these impacts and facilitate a return to pre-injury fitness levels. In this context, peptide therapies emerge as a promising avenue for enhancing tissue repair and regeneration.
By focusing research on the application and effects of specific peptides such as TB500 and BPC-157 Blend from Germany Direct Sarms, scientists can develop targeted interventions that accelerate healing, reduce downtime, and ultimately contribute to more effective recuperation methodologies for athletes and fitness enthusiasts.
Some of the common injuries that can benefit from the use of peptides for injury repair include:
When peptides for injury repair are considered during the repair process, different benefits may be noticed, including:
Although Germany research has indicated the above advantages, many peptides have not yet been approved for human consumption.
Peptides are made from at least 50 amino acids that are linked together. They are the building blocks of protein and provide plenty of functions in the body such as messaging and signalling. Some act like hormones, while others act like neurotransmitters. Peptides are known to bind to receptors which can be found on the cell surface and signal the other cells what to do. They are very specific making them safe and well-tolerated, and they can control or influence how the body reacts to physical exercises or even diet.
In the field of athletic and injury recovery research, it’s well-understood that individuals engaged in active lifestyles, sports, or physical activities inevitably face the risk of injuries. These injuries can significantly delay their return to normal activities, competitive sports, dance, or fitness routines. Optimizing injury recovery time while minimizing complications is a critical area of focus in regenerative medicine and sports science.
Germany Researchers have identified that specific biological agents, including peptides and growth hormone (GH) secretagogues, show promise in enhancing the body’s natural repair mechanisms. Such substances can effectively stimulate the secretion of growth hormones, instrumental in muscle fiber formation, cellular regeneration, and joint repair.
The use of GH secretagogues and peptides can therefore be a pivotal strategy in accelerating tissue repair and regeneration, facilitating a faster injury repair for individuals eager to resume their normal or athletic activities. This dynamic area of research holds potential not only for improving recovery timelines but also for advancing our understanding of tissue healing processes.
In injury repair research, scientists play a key role in uncovering how certain peptides, like BPC-157 and Thymosin Beta 4, speed up recovery. As regenerative medicine grows, these peptides’ role in boosting the body’s healing is crucial.
They offer unique benefits for tissue regeneration, reducing inflammation, and enhancing well-being. Understanding these peptides for injury repair is vital for researchers developing new injury recovery methods, advancing the field and improving rehabilitation strategies.
Thymosin Beta 4, or TB500, promotes the regeneration and movement of skin cells, blood vessels, and muscle cells, greatly improving wound healing and speeding up injury recovery. Originating from the thymus gland, its role in speeding up regeneration and its potential in injury recovery are key interests for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering researchers. Its action mechanism supports new therapeutic methods aimed at enhancing healing and recovery.
BPC-157 (Body Protection Compound 157) is widely regarded by research professionals as an effective agent for the rapid healing and recovery of muscle, tendon, and bone injuries. It can also help with various gastrointestinal issues, including ulcers and inflammatory bowel disease. These peptides for injury repair work by promoting the formation of new blood vessels and enhancing collagen production to speed up the healing process.
Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 or also known as IGF-1 is considered as the next generation in enhancing muscle building performance. It is the essential growth factor that your body produces even more than the Human Growth Factor (HGH).
Mechano Growth Factor or MGF is a potent inducer of muscle growth. It is responsible for causing trauma in the muscle cell to split resulting in the new creation of muscle cells as well as muscle repair and growth. Also, it plays a vital role in the growth of new cells and cell repair and recovery.
CJC-1295/Ipamorelin is a good combination of peptides due to a strong effect on the release of IGF-1 and Growth Hormone. It can reduce body fats employing forcing the body to burn the stored fats as a source of energy. Also, this peptide combination is also effective in increasing cellular repair, collagen production as well as regeneration. Discover ALL peptide blends from Direct Sarms.
Although physical injury will take time to go back to your usual activities, peptides can help you enhance recovery. Also, you will be able to improve your well-being and prevent any health risks.
Despite the advancing Germany research into peptides for injury repair, many are yet to be approved for human consumption. Peptides from Direct SARMs Germany are intended for research purposes only.
[1] I.Pountous et al (2016) The role of peptides in bone healing and regeneration: a systematic review – BMC Medicine, 14, Article number: 103 (2016).
[2] M.Zhang et al (2021) Repair of Peripheral Nerve Injury Using Hydrogels Based on Self-Assembled Peptides – Gels 2021, 7(4), 152.
ALL CONTENT AND PRODUCT INFORMATION AVAILABLE ON THIS WEBSITE IS FOR EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
DISCLAIMER: These products are intended solely as a research chemical only. This classification allows for their use only for research development and laboratory studies. The information available on our Germany Direct Sarms website is provided for educational purposes only. These products are not for human or animal use or consumption in any manner. Handling of these products should be limited to suitably qualified professionals. They are not to be classified as a drug, food, cosmetic, or medicinal product and must not be mislabelled or used as such.

Exploring the Potential of BPC-157 in Healing Knee Injuries The quest for more effective treatments for knee injuries is increasingly focusing on peptides like BPC-157,

Peptide stacking is a sophisticated method that involves the deliberate selection and combination of specific peptides to enhance their individual effects, leading to superior results
Worldwideshipping

Visa/Mastercard/Zelle
Cryptocurrency /Transfers

Safe and Secure Shopping

We Distribute
From

YOU MUST BE OVER 21 YEARS IN ORDER TO USE THIS WEBSITE. All of the products are to be handled only by properly trained and qualified LABORATORY or RESEARCH professionals.